Often called candles Hopi ear candles have been known since antiquity. They are used to clean the wax content in the ears. They are characterized by a cylindrical appearance, or coiled and are normally based on beeswax often enriched with essential oils and spread on a frame-to-frame average cotton.
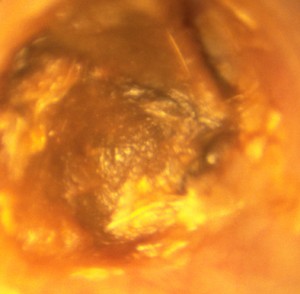
Sealingly placed at the entrance of the ear canal (Figure 6), the plug is intended to turn from the start of combustion, an effect of fumigation followed by a chimney effect suction eliminating the wax contained in the external auditory meatus. All this is an illusion.
A recent work [i] has been shown experimentally that there was no suction phenomenon when burning candles in a model of the external auditory canal with sensors. Similarly, attempts to extract wax candles with patients with a plug are all proved ineffective [ii].
Moreover, the wax residue highlighted after burning the candle is also found if the candle is burned without being applied to the input of the external auditory canal. The major drawback to the use of these candles is not ineffective but the problems they can cause: contact dermatitis at the entrance of the external auditory canal, burning the flag or the external auditory canal, partial occlusion total duct or by accumulation of wax from the candle and even perforation of the eardrum. These risks of injury are never mentioned in the advertisements for ear candles.
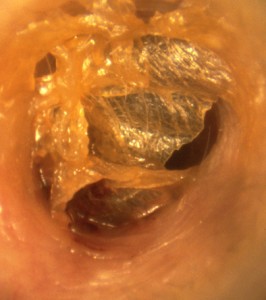
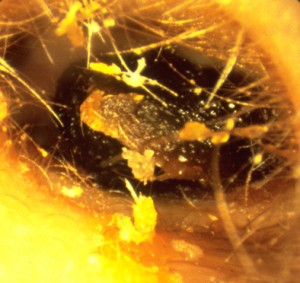
Moreover, very often, these candles cause deposits in the external auditory canal (Figure 7). These deposits will lead to an increase in the production of wax because they are considered foreign. Finally advertising falsely stated that these candles can be used to treat various diseases of the ear [iii], which is even more dangerous. They are not recommended for cleaning the ears is because the risks clearly outweigh the alleged benefits.
Sealingly placed at the entrance of the ear canal (Figure 6), the plug is intended to turn from the start of combustion, an effect of fumigation followed by a chimney effect suction eliminating the wax contained in the external auditory meatus. All this is an illusion.
A recent work [i] has been shown experimentally that there was no suction phenomenon when burning candles in a model of the external auditory canal with sensors. Similarly, attempts to extract wax candles with patients with a plug are all proved ineffective [ii].
Moreover, the wax residue highlighted after burning the candle is also found if the candle is burned without being applied to the input of the external auditory canal. The major drawback to the use of these candles is not ineffective but the problems they can cause: contact dermatitis at the entrance of the external auditory canal, burning the flag or the external auditory canal, partial occlusion total duct or by accumulation of wax from the candle and even perforation of the eardrum. These risks of injury are never mentioned in the advertisements for ear candles.
Moreover, very often, these candles cause deposits in the external auditory canal (Figure 7). These deposits will lead to an increase in the production of wax because they are considered foreign. Finally advertising falsely stated that these candles can be used to treat various diseases of the ear [iii], which is even more dangerous. They are not recommended for cleaning the ears is because the risks clearly outweigh the alleged benefits.